|
|||||||
|
|||||||
Ramy Home Page Home Page |
Ramy's ATM PAGE
ATM Definition: Asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) is a high-performance, cell-oriented switching and multiplexing technology that utilizes fixed-length packets to carry different types of traffic. ATM is a technology which will enable carriers to capitalize on a number of revenue opportunities through multiple ATM classes of services, high-speed local area network (LAN) interconnection, voice, video, and future multimedia applications in business markets in the short term and in community and residential markets in the longer term. Overview
Changes in the structure of the telecommunications industry and market conditions have brought new opportunities and challenges for network operators and public service providers. Networks which have been primarily focused on providing better voice services are evolving to meet new multimedia communications challenges and competitive pressures. Services based on asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) and synchronous digital hierarchy/synchronous optical network (SDH/SONET) architectures provide the flexible infrastructure essential for success in this evolving market (see Figure 1).
Figure 1:
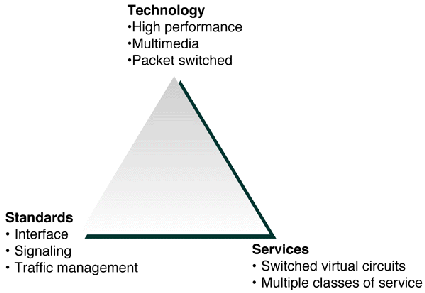
ATM, which was once envisioned as the technology of future public networks, is now a reality with service providers around the world introducing and rolling out ATM and ATM-based services. The ability to successfully exploit the benefits of ATM technology within the public network will provide strategic competitive advantage to both carriers and enterprises.
In addition to revenue opportunities, ATM reduces infrastructure costs through efficient bandwidth management, operational simplicity, and the consolidation of overlay networks. Carriers can no longer afford to go through the financial burden and time required to deploy a separate network for each new service requirement (e.g., dedicating a network for a single service such as transparent LAN or frame relay). ATM technology will allow core network stability while allowing service interfaces and other equipment to evolve rapidly.
The Intelligent and Fast Parallel Web Search
Ramy Home Page Home Page
Comment on this tutorial.
Last modified Thursday, 25-Feb-1999 12:44:24 CST
Copyright © 1999